Quick Overview: This blog talks about the pros and cons of Monolithic vs Microservices and how they are different from each other. It explains what is monolithic architecture in software development and helps new businesses and established companies pick the best architecture for growth and long-term success.
Many teams compare Monolithic vs Microservices when they build software in 2026. This choice changes how systems work. It also has an effect on how they grow over time. Companies want software that works quickly and reliably. They also want systems that are simple to change. The right architecture makes it easier for teams to reach these goals.
Recent research shows that about 74% of businesses use microservices right now. Teams pick this model so they can release things faster. It also works well with cloud services. Microservices make it easy for big apps to grow.
Microservices aren’t always the best choice, though. About 42% of businesses go back to simpler designs for some of their systems. They do this to save money. They also want to make things less complicated from a technical perspective. Because of this, monolithic vs microservices architecture for scalable applications remains an important topic.
More and more people are using microservices. At the same time, emerging companies still want cloud-native monolithic architecture. It’s easier to handle and costs less. It also works well for small groups. The best software architecture in 2026 will depend on clear goals and plans for the future.
What Is Monolithic Architecture?
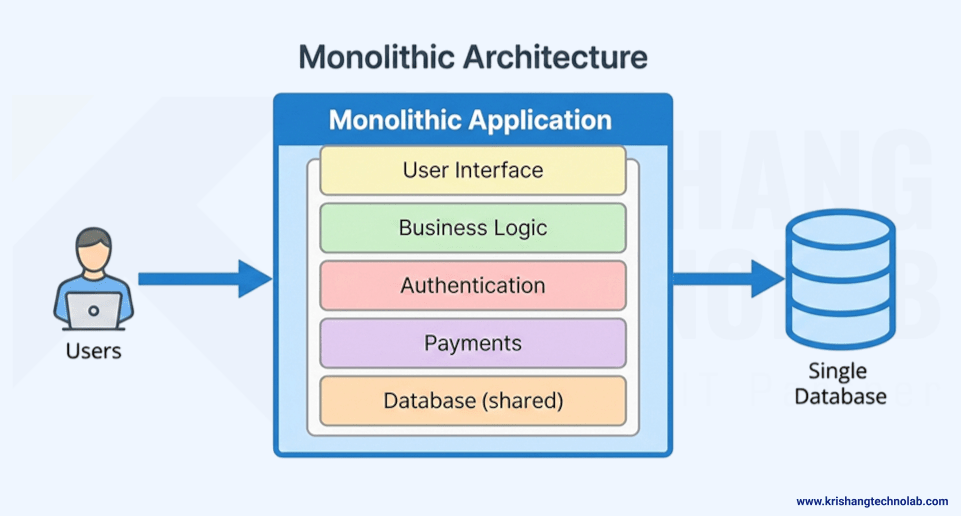
Building software with monolithic architecture is easy. Developers create the entire app as a single unit. The user interface, business logic, and data all reside in a single codebase.
This design makes it easier for software developers to switch to monolithic architecture. Developers can also quickly build, test, and deploy the app. Many iOS development service teams create small mobile apps using a monolithic architecture. But as the app gets bigger, it gets harder to take care of. Also, it takes more work to scale the app. If no one on your team has ever designed software before, you might want to hire Android Developers to help them work quickly on large apps.
Key Characteristics of Monolithic Applications
All of the features of monolithic apps are in one system. Parts work together very well. Because of this, early development goes quickly. But this makes it harder to be flexible with bigger projects. A small change in one part can change the whole app.
When you choose a monolithic architecture to construct big apps, it might be hard to expand because the parts are tightly connected. Also, maintenance grows harder as time goes on.
Some important features are:
- Single Codebase: All the UI, business logic, and data are in one place.
- Tightly Coupled Components: Changes in one module have an effect on others.
- Single Deployment Unit: Developers put the whole app into one file or package.
- Shared Resources: All of the modules use the same server, database, and infrastructure.
Advantages of Monolithic Architecture
It’s simple to understand and work with monolithic architecture. It’s easier for developers to test, debug, and deploy. Also, all the code is in one place, so it’s easy to find problems.
It also helps early development go faster. Teams don’t have to worry about how to talk to more than one service. So, many startups use monolithic systems because they are cheap to build. Also, this method saves small teams time and money.
The main benefits are:
- Simplicity: It’s easy to build, test, and keep up with.
- Faster Early Development: It’s easier to manage fewer services than more.
- Simplified Testing and Debugging: It’s easy to find bugs in one codebase.
- Lower Initial Cost: Less money spent on tools and infrastructure.
You can hire iOS Developers to help you set up a monolithic system quickly and easily if you need help.
Disadvantages of Monolithic Architecture
It’s tougher to expand monolithic systems as apps get bigger. For example, developers have to make the whole software bigger if one feature needs more resources. This makes things less efficient and more expensive.
It also takes longer to develop with huge codebases. If you need to rewrite a significant amount of code to integrate new tools, you risk becoming mired in technology. Another concern is dependability. Because of this, one defect can crash the whole system.
Common difficulties include:
- Bad scalability: Developers have to scale the complete program at once.
- Slow Development at Scale: It’s difficult to introduce changes to large codebases.
- Technology Lock-in: It’s hard to move to new frameworks.
- Less Reliable: A single bug can cause the whole system to crash.
- Problems with deployment: To upgrade the app, you have to redeploy everything.
What Is Microservices Architecture?
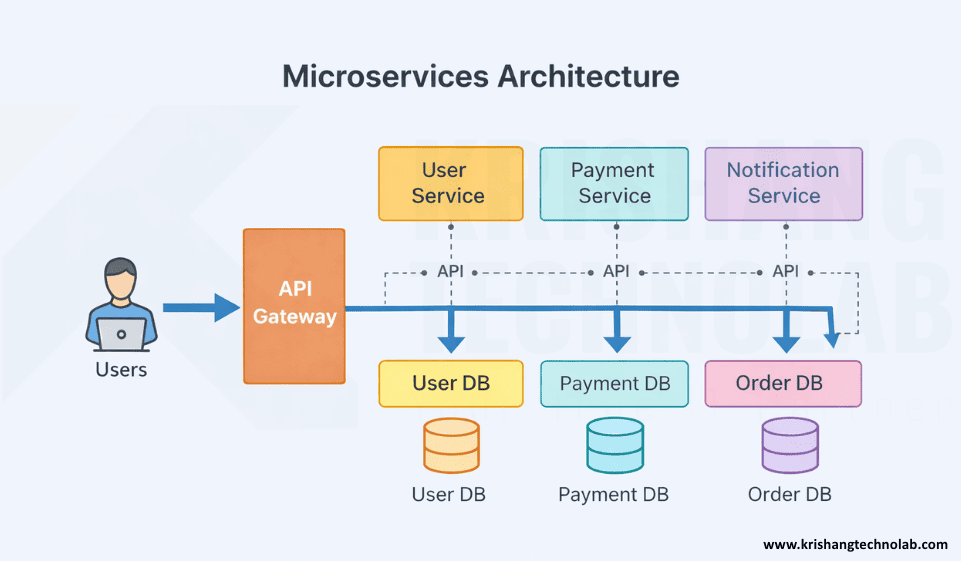
Microservices break apps down into smaller pieces. Also, each part has a job to do. After that, each part works on its own. Parts talk to each other through simple APIs. So, the app can be used in many ways. It is also simple to change.
Monolithic apps keep everything in one place. Microservices vs monolithic architecture, on the other hand, lets teams build and run parts on their own. Microservices also make things faster and more stable and give you more tech options. But it can be harder to deal with a lot of parts. Also, Flutter App Development Services teams can make apps faster with microservices.
Core Principles of Microservices
Microservices feature easy-to-follow rules. These principles also assist teams in staying up to date on the newest developments in software architecture. For example, they make it easier to build apps and make them bigger.
- Single Responsibility Principle: Each part only does one thing, like handling users or orders.
- Autonomy & Independence: Teams can run and update parts without stopping other teams.
- Decentralized Governance: Each team chooses a different language or database for each part.
- Data Separation: Each part has its own data.
- API-Driven Communication: Parts talk to each other using simple APIs like REST.
Advantages of Microservices Architecture
Microservices have a lot of good things about them. Teams can also make changes more quickly. Next, teams that provide mobile app development services can safely try out new tools. Microservices also make apps more stable.
- Scalability: Each team makes its own part bigger.
- Faster Releases: Teams swiftly add new functionality.
- Tech Variety: Teams pick the best tech for each part.
- Fault Isolation: The app keeps working even if one part breaks.
- Easier Maintenance: Small code is easy to work with.
Disadvantages of Microservices Architecture
There are some problems with microservices. For instance, skilled teams are needed to handle a lot of parts. Also, it takes longer to test and watch parts. Next, tasks that cross parts need to be done with care. So, teams need the right tools.
- Operational Complexity: The team will have to watch and operate on numerous sections of code.
- Distributed Tasks: The team’s task is to make various sections compatible with one another.
- Testing Overhead: A team that does not spend adequate time testing applications.
- Network Delays: Implementing system communication over networks may cause significant slowdowns in application responses.
- Data Challenges: The team must ensure accurate data sharing across sections of the application.
Monolithic vs Microservices: Key Differences Explained
Two different ways to create software are monolithic and microservices. First, a monolithic architecture puts everything in one place. The codebase for the whole app is in one place. This makes it easy to get started. Teams can build quickly. But growth can also cause problems. A small change can have an effect on the whole app.
Microservices architecture, on the other hand, splits the app into small services. Each service has just one job. These services use APIs to talk to each other. Because of this, development teams send out updates more quickly. They only scale what they need to. Microservices are better for big apps because of this. Many teams, like a React Native app development company, use this model to grow over time.
Core Differences at a Glance: Monolithic vs Microservices
| Feature | Monolithic Architecture | Microservices Architecture |
| Structure | A single codebase and process that works for everyone. | A group of independent services that aren’t tightly linked. |
| Deployment | Deployed as one unit, like a JAR or WAR file. | You can deploy each service on its own. |
| Scalability | The whole application must scale at once. | Each service scales based on how much demand there is. |
| Fault Tolerance | One mistake can bring down the whole system. | Failures only happen in one service. |
| Technology | Uses a single shared set of tools. | Let each service use its own tech stack. |
| Database | Uses one central database that everyone can use. | Each service has its database. |
How to Transition from Monolithic to Microservices Architecture
It takes careful planning to switch from a monolithic system to microservices. First and foremost, the goal is to lower risk. The business must also keep going. The best way to move in 2026 is step by step. Teams take out services one at a time, in other words. This method avoids the risk of a full rewrite.

1. Preparation and Assessment
- Audit the Monolith: First, learn about the system as it is now. Make a map of all the data flows and dependencies. Also, find modules that are tightly linked. Tools like New Relic and Dynatrace help you see how requests move through the codebase. As a result, teams can see things more clearly.
- Define Boundaries: Next, use Domain-Driven Design (DDD). This helps find contexts that are limited. Some of these contexts are Payments or Inventory. Every area can work by itself. So, the limits of the service become clearer.
- Establish Infrastructure: Before you move, make sure you have the right tools. For instance, use Jenkins or GitLab CI to make CI/CD pipelines. After that, use Docker to put things in containers. Finally, add Kubernetes to manage everything. This base will help you grow in the future.
2. Migration Strategies
- Strangler Fig Pattern: Start by building new microservices around the monolith. After that, send traffic through an API gateway like Kong or NGINX. The monolith, on the other hand, is still in charge of old features. New services take the place of old ones over time.
- Branch by Abstraction: Another choice is Branch by Abstraction. In this case, you add an abstraction layer to the monolith. At first, calls go to codes that are already there. Later, you will switch them to the new microservice. Changes are kept under control as a result.
- Parallel Run Pattern: Sometimes, run both systems at the same time. This means that the old and new systems can work together. After that, verify the results to confirm that they are correct. Finally, send all of the traffic to the new system.
3. Data Layer Transition
- Database per Service: Every microservice should have its own database. This design makes things less connected. It also lets you scale things on your own. So, services can still be flexible.
- Synchronization: Data must stay the same during migration. Because of this, use methods that are based on events. Tools like Change Data Capture (CDC) and Apache Kafka work well. This keeps systems in sync.
- Manage Transactions: Distributed transactions make things more complicated. Use the Saga Pattern to address this. This pattern uses actions that make up for other actions. If one step doesn’t work, the next one will. So, the data stays the same.
4. Implementation Steps
- Extract Low-Risk Services: Start with a small amount. First, move services that aren’t important, like Notifications or Reporting. This makes the risk lower. It also helps check the migration process early on.
- Decouple Vertically: Extract all of the features of the application, i.e., the UI, business logic and data, into one full-featured service so that all of the service’s components are contained in one service. This allows the service to be owned by one team.
- Implement Inter-Service Communication: Use REST or gRPC for direct requests. For processes that run in the background, use message queues like RabbitMQ. This combination makes things work better and more reliably.
- Monitor and Iterate: Use Prometheus and Grafana to keep an eye on metrics. Look at how well things worked before and after each change. Then, keep getting better.
When to Choose Monolithic vs Microservices Architecture
Monolithic architecture works well for small teams and new businesses. First, it helps teams build quickly. The setup is still easy. So, working every day seems easy. Many companies hire Android developers so they can quickly load apps on one system.
Microservices architecture is beneficial for apps that want to grow quickly. Next, it works with cloud and SaaS systems. Because of this, teams send out updates more often. It also seems easier to scale. Many businesses hire iOS developers to make apps. Then, to make sure they follow best practices for microservices, they hire Flutter app developers.
Important Things to Think About:
- Size of the project now and in the future
- Need for quick updates
- Ability to run cloud systems
Final Thoughts: Monolithic vs Microservices in 2026
Choosing monolithic vs microservices is an important decision. First, monolithic architecture is good for small groups. It also works for projects that are just getting started. Teams can build things faster and test them more easily. Also, the time it takes to set up stays low. Many new businesses have chosen this model because of it. In the microservices vs monolithic comparison, monolithic perform better when speed is the main goal. Because of this, development teams spend more time working on features.
On the other hand, microservices design works well for businesses that grow quickly. Each part can grow bigger on its own. You can grow faster with this. Teams also report things more often. It will be very important for software architecture in 2026 to be able to change quickly. Because of this, apps that get a lot of traffic often use microservices. Krishang Technolab has experts who help teams pick the best software development architecture. They will be able to grow over time with the help of their knowledge of scalable systems and Android Development Services.
FAQs: Monolithic vs Microservices
What is monolithic architecture in software development?
Building software with a monolithic architecture is easy. There is only one codebase for all features. The app works as one unit. First, it works well for small groups. It also lets you develop quickly. Because of this, many startups choose monolithic apps to save time and work.
How do microservices differ from monolithic architecture?
Microservices split an app into smaller parts. Every service has a single task. Service can talk to each other through APIs. On the other hand, monolithic apps keep everything in one place.
Important differences:
- Independent scaling in microservices
- Single deployment in monolithic apps
- More flexibility with microservices
So, microservices help teams work faster on each service.
Are microservices better than monolithic for cloud-based apps?
Yes, microservices are great for apps that run in the cloud. They are easy to scale and can handle traffic spikes. Also, each service can grow on its own. But you need to be good at DevOps. This answer makes it clear that microservices are better than monolithic for cloud-based apps.
What are the benefits of microservices for scalable apps in 2026?
Microservices help businesses grow quickly. They help teams move quickly. They also lower risk. The main benefits are:
- Better scalability
- Faster updates
- Fault isolation
So, microservices are great for apps that need to grow in 2026.
What challenges does monolithic architecture face in 2026?
As apps get bigger, it’s hard to manage monolithic. Also, a small change can effect the whole system. Scaling costs more. Because of this, monolithic architecture often causes problems for big apps in 2026.
How to safely transition from monolithic to microservices architecture?
The move should happen slowly. Teams shouldn’t hurry. First, break up features slowly. Next, talk to each other using APIs. Last but not least, make sure to test each service thoroughly.
This shows how to move from a monolithic architecture to a microservices architecture in a safe way.